how do you test for testicular torsion|is testicular torsion obvious : importer Testicular torsion. During testicular torsion a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that brings blood to the scrotum, the loose bag of skin under the penis that . web🎀 About Me 🎀 (self.ThereSimmer) submitted 5 minutes ago by ThereSimmer - pinned. Hello there! I’m 19 years old and living the boring a life of a nursing student 🩺 here in LA. My .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Nova linha de ônibus BRT começa a circular no corredor Trancarioca nesta terça Serviço liga a Ilha do Fundão até a estação Santa Efigênia, na Taquara Por Meia Hora
Diagnosis. Your doctor will ask you questions to verify whether your signs and symptoms are caused by testicular torsion or something else. Doctors often diagnose testicular torsion with a physical exam of the scrotum, testicles, abdomen and groin. Your doctor .Testicular torsion. During testicular torsion a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic . Testicular torsion. During testicular torsion a testicle rotates, twisting the spermatic cord that brings blood to the scrotum, the loose bag of skin under the penis that .
volumetric karl fischer titrator Brand manufacturer
Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding. A history and physical exam consistent with testicular torsion mandates an immediate surgical consult for scrotal exploration. If history and physical exam suggest .
Testicular torsion is when the spermatic cord above your testicle twists, cutting off blood flow to your testicle. Testicular torsion can happen at any age, but it most often happens to boys .Testicular torsion is an emergency condition due to rotation of the testis and consequent strangulation of its blood supply. Symptoms are acute scrotal pain and swelling, nausea, and vomiting. Diagnosis is based on physical . Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord becomes twisted. This causes a restriction in blood flow to the testes, severe pain, and possibly permanent damage.
A doctor's examination and sometimes ultrasonography are needed for testicular torsion diagnosis. Treatment is to untwist the spermatic cord. What Is Testicular Torsion? Testicular torsion usually occurs in boys between the ages of . How does a doctor check for testicular torsion? To check for testicular torsion, a doctor will examine your testicles, scrotum, groin, and abdomen.
Testicular torsion is a very serious condition and is considered a medical emergency. Rotation of the testicle around the spermatic cord can cause obstruction of the arterial blood flow to the testicle, as well as the venous . Testicular torsion occurs when a testis torts on the spermatic cord resulting in the cutting off of blood supply. The most common symptom is acute testicular pain and the most common underlying cause, a bell-clapper deformity. The diagnosis is often made clinically but if it is in doubt, an ultrasound is helpful in confirming the diagnosis. . The test can show if you have testicular torsion. Testicular torsion is a twisting of the testicle that can cut off blood flow. If ultrasound with color Doppler shows lower blood flow to a testicle than is typical, the testicle is twisted. If blood flow is higher than typical, this can help confirm that you have epididymitis.Testicular torsion is when the spermatic cord above your testicle twists, cutting off blood flow to your testicle. Testicular torsion can happen at any age, but it most often happens to boys ages 12 to 18 or babies. Without blood supply, the tissue of your testicle can die in a few hours . See a doctor right away if you think you have .
Testicular torsion, or twisted testicle, can be extremely painful. . A healthcare professional may also test the patient’s cremasteric reflex, which is highly effective in helping diagnose . Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, and/or necrosis of testicular tissue. Laher A, Ragavan S, Mehta P, et al. Testicular torsion in the emergency room: A review of detection and management strategies.
How common is testicular torsion? Testicular torsion occurs in teenage boys aged 13-18 years. This is found to happen in around 1 in 4,000 young men. Newborn babies and younger children sometimes develop this problem. It is uncommon over the age of 25 but does occur sometimes in older adults and can occur at any age.
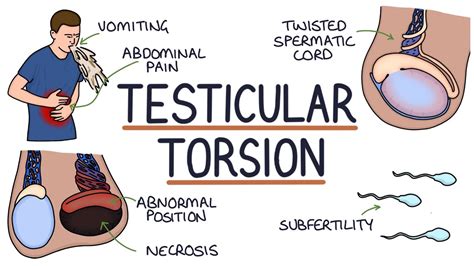
Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord (from which the testicle is suspended) twists, cutting off the blood supply to the testicle. [3] The most common symptom in children is sudden, severe testicular pain. [1] The testicle may be higher than usual in the scrotum and vomiting may occur. [1] [2] In newborns, pain is often absent and instead the scrotum may become .What is testicular torsion? Testicular torsion happens when one of your testicles twists around. Each testicle is attached to a spermatic cord, which contains blood vessels that carry blood to the testicle. In testicular torsion, this becomes twisted (called torsion) and blocks the flow of blood to the testicle. Testicular torsion is an emergency. No special preparation is necessary to do a testicular self-exam. You might find a testicular self-exam is easier during or after a warm bath or shower. Heat relaxes the scrotum, making it easier for you to check for anything unusual. What you can expect. To do a testicular self-exam, stand unclothed in front of a mirror. Then: Look for swelling.
Causes of testicular torsion. There are two mechanisms for testicular torsion, intravaginal and extravaginal. Intravaginal. Intravaginal torsion occurs due to a lack of fixation of the posterolateral section of the testis to the inner wall of the scrotum.. This occurs due to a higher than usual attachment point of the tunica vaginalis to the testis and epididymis within the sac.This video contains a visual explanation of testicular torsion, aimed at helping students of medicine and healthcare professionals prepare for exams. Written.Testicular torsion can occur at any age, although it is more common in the first year of life and at puberty (peak age being 12-18 years). Testicular torsion can even occur before birth (during the prenatal period). Left testicle torsion is more common than right testicle torsion. The exact cause of testicular torsion is not known.
Testicular torsion is a painful twisting of a boy’s testicles and spermatic cord. Torsion causes blood to not flow to the testicles. This can damage them. Treatment needs to be done right away to prevent long-lasting (permanent) injury to the testicles. . Know why a test or procedure is recommended and what the results could mean. Testicular torsion is a time-dependent diagnosis, a true urologic emergency, and early evaluation can assist in urologic intervention to prevent testicular loss. Ultrasound is the ideal imaging modality to evaluate the scrotal contents. . Ultrasound is not a perfect test for testicular torsion, especially in the very young. For example, 40% .Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for 10% to 15% of
A diagnosis of testicular torsion should be suspected in any person presenting with acute scrotal pain and/or swelling, before other causes are considered.. Ask about:. Any scrotal pain — the location (including unilateral or bilateral), nature, radiation to surrounding structures, speed of onset, duration, severity, exacerbating factors (such as activity or positional changes).
Testicular torsion is a urological emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischaemia, and/or necrosis of testicular tissue. Laher A, Ragavan S, Mehta P, et al. Testicular torsion in the emergency room: A review of detection and management strategies. Each year, testicular torsion affects one in 4,000 males younger than 25 years. Early diagnosis and definitive management are the keys to avoid testicular loss. All prepubertal and young adult .
Testicular torsion treatment. To diagnose testicular torsion, a doctor (often a urologist) evaluate the groin and scrotum area. The doctor will also check the abdomen. You may need an ultrasound to confirm the diagnosis. (An ultrasound creates an image with soundwaves). It allows the doctor to monitor blood flow and look for twisting.Although testicular cancer is rare in teenage guys, overall it is the most common cancer in males between the ages of 15 and 35. It's important to try to do a TSE every month so you can become familiar with the normal size and shape of your testicles, making it easier to tell if something feels different in the future.American Urological Association Curriculum on Acute Scrotum: This case-study offering from the association's medical school curriculum covers the differential diagnosis of acute scrotum with a concentration on 6 conditions: epididymitis, hernia, scrotal trauma, testicular torsion, testicular tumor, and torsion of testicular appendices.Had my younger self read this post, maybe I'd still have two balls and one less traumatic experience. So if you're reading this and you ever wake up feeling like you've been kicked in the nuts, please see a doctor immediately. It is not normal and even if you puke the whole way there, it will absolutely be worth it.
It is vital that boys and men know that pain in their testicles could be a sign of testicular torsion. If you notice your child or teen experiencing these symptoms, they should head to the hospital straight away. How is testicular torsion treated? The only treatment for testicular torsion is an urgent operation. When you arrive at the hospital .Anatomy of the normal testis, bell clapper anomaly and intravaginal testicular torsion. Blue testis, Green epididymis, Lavender spermatic cord and vessels, Red tunica vaginalis. Normally, the epididymis extends along the full length of the testis posterolaterally so that the upper and lower poles of the testis are covered and the tunica vaginalis parietal lamina is anchored to the .Doctors suspect epididymitis or epididymo-orchitis based on a physical examination. They'll usually also do: A urine test to look for infection. Sometimes, ultrasound, to be sure that you don't have a twisted testicle (testicular torsion)
Investigations. The diagnosis of testicular torsion is a clinical one, therefore any suspected cases should be taken straight to theatre for scrotal exploration.. However, in cases with sufficient equipoise, Doppler ultrasound (Fig. 4) can be used to investigate potential compromised blood flow to the testis (if available, this test has a high sensitivity (89%) and .
testicular torsion signs on examination
Resultado da Estratégias Eficientes para a Gestão de Perdas em Cassinos Online. Navegando nas Águas da Probabilidade: Ganhos e Perdas nos Cassinos .
how do you test for testicular torsion|is testicular torsion obvious